Movement After Position
The Principle: “We may take it then that an army without its baggage-train is lost; without provisions it is lost; without bases of supply it is lost.” — Sun Tzu
The Art of Coordinated Movement
A cybersecurity team detects a breach at 2 AM. They have the skills, the tools, and the authority to act. But without coordination, that capability becomes chaos, analysts duplicating work, containment efforts conflicting, and communication breaking down. By dawn, the advantage is gone.
In February 1943, American forces faced German tanks at Kasserine Pass in North Africa. They had the weapons, the numbers, the training. What they lacked was coordination between units and effective air-ground communication. The result? The first major American defeat of WWII was not due to a lack of capability, but to failure to maneuver as a unified force.
Fifteen months later, those same American forces learned the lesson. On June 6, 1944, D-Day coordinated 12 nations, over 7,000 vessels, and 160,000 troops across five beaches in a single operation. Not because they suddenly acquired better weapons, but because they mastered maneuvering. Kasserine Pass taught them that capability without coordination is chaos. Normandy proved that coordination transforms capability into victory.
Eighty years later, the battlefield is digital, but the lesson remains the same.
Sun Tzu called this the difference between movement and maneuvering.
Maneuvering is the discipline of transforming positional advantage into progress without depleting resources. Though movement may appear straightforward (advance, pivot, respond), it demands careful coordination. Without coordination, movement breeds confusion and disorder, undermining any initial advantage.
In Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu, there’s a fundamental principle: position before submission. A novice rushes for the choke. A master secures the proper position, seeks control, applies the proper pressure, isolates the arm, and then the finish is there for the taking. The submission becomes inevitable because the position made it so.
Maneuvering works the same way: structured movement from an established position. Not frenetic action. Coordinated, calculated movement in advance.
Whether in military operations, government, or cybersecurity, the true challenge lies in maintaining momentum while preserving balance. Effective teams favor structured, intentional movement, not just speed.
This is the heart of maneuvering: composure, intent, and clarity. Act from principle, not anxiety.
The Maneuvering Decision Matrix
Sun Tzu understood that effective maneuvering requires reading the moment, knowing when to accelerate, when to pause, and when to let the environment dictate pace.
Modern leaders need the same discernment:
When to Accelerate:
- The advantage is clear and actionable.
- Resources are sufficient.
- Team alignment is strong.
- Opponent is vulnerable
When to Pause:
- Visibility is degraded
- Fatigue is setting in across the team.
- Purpose has become uncertain.
- Information remains incomplete
When to Let Environment Dictate:
- The opponent is making mistakes.
- Terrain is shifting faster than you can control
- Patience offers a strategic advantage.
- Reactive movement would expose weakness.
This isn’t indecision. It’s tactical discipline. The fighter who controls tempo controls the outcome.
Tempo and Terrain
In both war and cybersecurity, timing determines outcomes more than sheer speed. When to act matters more than how quickly you act.
Sun Tzu cautioned that armies advancing too rapidly become fatigued, while those moving too slowly forfeit initiative. Balance requires understanding rhythm, discerning when to accelerate, when to pause, and when to let the environment set the pace.
Today, that terrain is digital.
The modern battlefield consists of networks, cloud environments, and global systems. Effective cybersecurity professionals study the digital landscape to move with intent, not to avoid movement altogether.
In the cloud era, terrain isn’t geography, it’s architecture.
Latency, visibility, and complexity shape what’s possible. The most secure organizations extend beyond perimeter defense by developing a comprehensive understanding of their operational landscape. They design systems where quick tactical movements don’t create strategic vulnerabilities.
The Cyber Battlefield: Coordination Over Chaos
In cybersecurity, effective maneuvering means more than quick patching or immediate responses. It requires aligning teams, especially during high-pressure situations.
- Incident response represents maneuvering under pressure: containment, communication, and recovery.
- Threat intelligence involves maneuvering through uncertainty—transforming fragmented information into actionable insights without prematurely acting on incomplete data.
- Automation functions as the logistical backbone, the supply chain supporting frontline operations. When automation fails, even highly skilled analysts face burnout.
Many security operations centers (SOCs) miss this point. Constant urgency and nonstop action may seem productive, but endless motion risks exhaustion and reduced effectiveness.
Authentic maneuvering is characterized by calm, control, deliberation, and focus.
- Wing Chun’s centerline theory offers a simple, direct, economical model. SOC analysts don’t need fifty tools—they need the right three, automated properly, with clear escalation paths. Economy of force.
- The central point: when your playbook drives decisions, you maneuver. When alerts drive decisions, you react.
Cloud Mobility: The Terrain in Flux
The shift to cloud computing redefined what “maneuvering” means. In the old world, servers stayed put. Now, data, workloads, and identities move across providers, borders, and legal frameworks.
In this environment, organizational strength comes not from rigidly restricting movement, but from orchestrating secure and transparent operations.
Cloud maneuvering looks like:
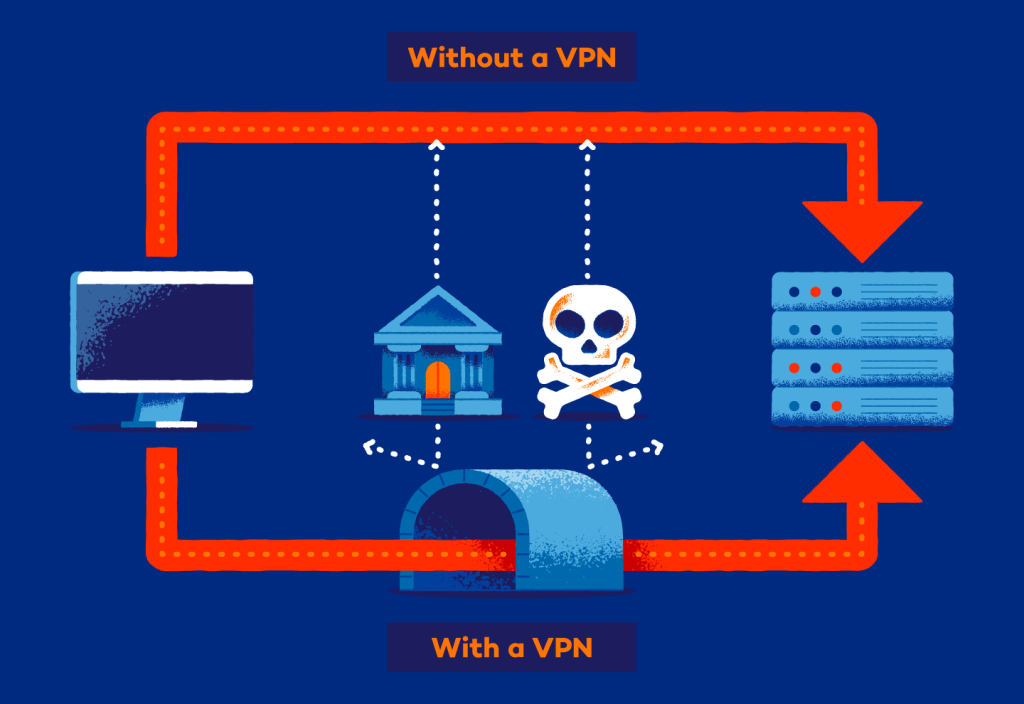
- Workloads shifting across regions without breaking compliance
- Data flowing securely through APIs without leaving blind spots
- Teams pivoting incident response playbooks across hybrid environments in real time
Cloud environments reward planning for motion. Organizations win by designing for agile, secure movement, not by resisting change.
In 2023, a Fortune 500 company’s cloud migration stalled not because of technical limitations, but because their security team designed for a static perimeter. When workloads needed to shift regions for compliance, every move required manual review.
Organizations that assume static conditions are at a disadvantage.
This aligns with the martial principle of flow: Rigid fighters’ break. Rigid systems break faster.
Foreign Policy and the Cost of Motion
Nations, too, confuse movement with progress. America’s 20th-century record is full of lessons in tempo and fatigue.
But no example better illustrates the danger of resource-driven maneuvering than what led to the attack on Pearl Harbor.
The Pearl Harbor Lesson: When Resources Force Your Hand
Japan’s attack wasn’t born from ambition, it was forced by logistics. The U.S., Britain, and the Dutch enforced the ABCD embargo, cutting off:
- Oil
- Rice
- Steel
- Rubber
- Machine parts
Japan imported 90% of its oil. Cut off from fuel, it faced two choices: fight or run out of energy and food entirely.
Sun Tzu wrote: “Throw your men into death ground, and they will fight.”
Japan was placed on death ground by resource denial. Their maneuver, the attack itself, was coordinated brilliantly. Six aircraft carriers, 353 aircraft, precise timing across multiple strike waves.
Tactically, it was masterful.
But strategically? Admiral Yamamoto knew: “I fear all we have done is awaken a sleeping giant.”
A lingering question remains: was America truly sleeping? WWI had concluded only 20 years earlier. Before WWII, WWI was considered the deadliest war in human history, earning the moniker “The Great War” for its immense scale and death toll of approximately 20 million lives. Its unprecedented destruction set it apart from previous conflicts. So, America was hardly asleep. Back to Pearl Harbor.
The lesson isn’t about the attack’s execution. It’s about what happens when maneuvering is dictated by desperation rather than position. When resources force your hand, even perfect coordination can’t save you.
Sun Tzu’s calculus applies: survival-driven movement, no matter how well-executed, is still reactive. And reactive maneuvering rarely wins wars.
The United States later encountered similar challenges in Vietnam, Iraq, and Afghanistan, where rapid action outpaced strategic learning. Momentum itself became a compelling but hazardous force.
Diplomacy is maneuvering in another realm.
In contrast, contemporary policy frequently equates reaction with strategy, prompting responses to every crisis even when restraint or delay might prove more advantageous.
Sun Tzu’s wisdom cuts through centuries: “If you know neither the terrain nor the season, you march to fatigue, not to victory.”
The Logistics of Cyber Power
For cybersecurity professionals, logistics consists not of physical supplies, but of bandwidth, personnel, and operational clarity.
Sustained operations aren’t feasible if systems are overburdened, personnel remain on constant alert, and every issue is treated as critical.
Good logistics in cyberspace means disciplined prioritization:
- Which assets are mission-critical?
- Which alerts deserve escalation?
- What response cadence prevents burnout?
Sun Tzu would call this “feeding the army.” In today’s language, it’s resource stewardship.
An effective CISO ensures security professionals maintain resilience and don’t become exhausted before adversaries lose their resolve.
The data shows progress. Organizations took an average of 241 days to identify and contain breaches in 2025, down from 287 days in 2021. Not because threats got easier, but because purple-teamers got better at coordinated response. They learned to maneuver.
Maneuvering the Human Factor
The most challenging aspect of coordination isn’t the technical infrastructure; it’s the human element. While individuals contribute creativity, they also introduce unpredictability.
The numbers confirm what practitioners already know: 88% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. Not zero-days. Not sophisticated malware. Human mistakes. The technology isn’t the weak link—the coordination of people using that technology is.
Sun Tzu understood morale as a weapon system. He coordinated hearts and minds before he coordinated units.
The same applies to martial arts and security culture.
- In Muay Thai, they call it ring generalship, the fighter who controls space controls pace. The same applies to security teams. Leaders who set tempo, who decide when to press and when to absorb pressure, create the conditions for team effectiveness.
- The most effective cybersecurity teams operate like jazz ensembles, distributed but synchronized. Training, communication, and trust are the modern equivalents of morale.
This is modern maneuvering: achieving precision in movement without relying solely on hierarchical control.
The Risk of Endless Marching
Sun Tzu cautioned that armies remaining in the field for extended periods experience internal decline. This phenomenon appears today as burnout, alert fatigue, and continuous red team exercises that fail to produce lasting improvements.
Organizations that never rest eventually turn on themselves. This applies equally to companies and nations.
Movement should support strategic objectives, not substitute for them. Effective leadership requires recognizing when to pause, regroup, and restore organizational strength.
Without periodic rest, strength deteriorates into strain, and resilience devolves into attrition.
The Bridge to Variation
The final lesson of maneuvering emphasizes humility: movement does not constitute mastery; it serves as its test.
Any army, individual, or system that acquires the ability to move must subsequently develop adaptability: the capacity to alter rhythm, diversify tactics, and confound adversaries who anticipate predictability.
Leading us back to the initial principle: “We may take it then that an army without its baggage-train is lost; without provisions it is lost; without bases of supply it is lost.”
Maneuvering determines survival. Variation determines victory.
But first, you must learn to move without falling apart. Master coordination before you attempt improvisation. Secure your supply lines before you advance.
Because, as Sun Tzu understood, an army that moves with discipline can adapt. An army that moves with chaos can only collapse. The next chapter explores variation, but only those who’ve mastered maneuvering will recognize when to use it.