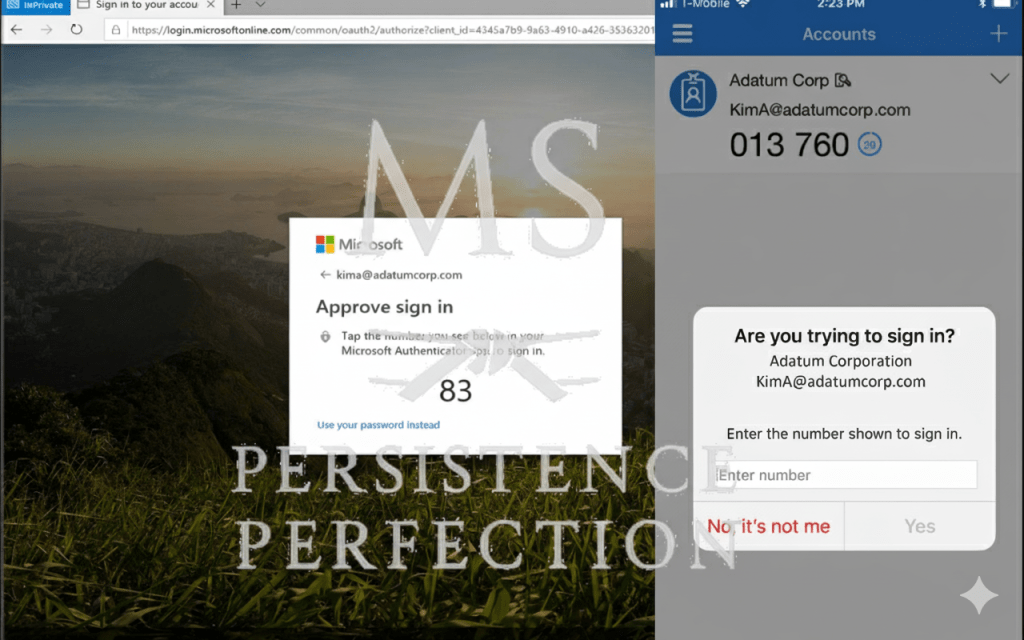
The Principles:
“The good fighters of old first put themselves beyond the possibility of defeat, and then waited for an opportunity of defeating the enemy.”
“Thus it is that in war the victorious strategist only seeks battle after the victory has been secured, whereas he who is destined to be defeated, first fights, and afterwards looks for victory.” —Sun Tzu
Every data breach, foreign conflict, and policy error typically originates from an action taken without adequate prior positioning.
There is a common tendency to conflate activity with progress. Sun Tzu recognized that true invincibility is rooted in defense, while the opportunity for victory depends on the adversary.
In contemporary terms, this concept is referred to as defensive posture: the disciplined practice of preparation prior to visibility.
Defensive Positions
Effective cybersecurity teams secure their positions well in advance of any actual test. They maintain comprehensive awareness of data locations, access privileges, and the criticality of various systems. Such teams implement patches discreetly, monitor systems consistently, and design infrastructures to recover from failures rather than assuming failures will not occur.
That’s tactical disposition:
- Enforcing least privilege to build resilience.
- Applying timely patching to keep critical systems protected.
- Building backups as integrated mechanisms for redundancy and recovery.
- Running tabletop exercises to rehearse scenarios that organizations hope never occur.
This often-invisible work may appear inconsequential until it proves essential in critical moments.
When Nations Forget the Same Lesson
Historical evidence indicates that both nations and organizations seldom pause sufficiently to engage in strategic reflection.
Nations often amass extensive arsenals, initiate large-scale programs, and extend supply lines to project strength. However, when strength is dispersed excessively, it transforms into fragility, a phenomenon known as overreach. Overreach fundamentally undermines resilience.
The United States has frequently responded to perceived threats with disproportionate measures, conflating activity with effective strategy and reallocating resources without a long-term perspective. Engagements in wars and alliances often occur more rapidly than preparations for their potential consequences.
The consequences include wasted resources, public fatigue, and strategic exhaustion. All of which contribute to diminished geopolitical and geostrategic self-awareness.
According to Sun Tzu, achieving invincibility does not involve amassing weapons, engaging in unnecessary interventions, or imposing ineffective sanctions. Instead, it requires constructing economic, digital, and diplomatic systems capable of absorbing shocks while maintaining integrity. A resilient nation need not swing at every shadow.
Resource Stewardship
Cybersecurity is frequently perceived as a process of continual escalation, characterized by the addition of more tools, dashboards, and alerts.
However, each new platform introduces additional complexity, which in turn creates new potential attack surfaces.
Effective security practices may require declining adoption of the latest technologies and decommissioning unnecessary systems to simplify complex environments.
As Bruce Lee once said “I fear not the man who has practiced 10,000 kicks once, but I fear the man who has practiced one kick 10,000 times.”
Simplifying operations enables organizations to concentrate on mastering essential tools, particularly when resources are limited. The principles of simplicity, directness, and economy of motion are fundamental to effective practice.
Our government should also learn to exercise the same restraint. Faithful stewardship isn’t constant investment in everything; it’s a deliberate focus on what matters most.
This approach exemplifies strategic minimalism, which emphasizes the optimal utilization of public resources and, ultimately, enriches us all by conserving precious and limited resources.

Similarly, as America’s original Foreign Policy was initially articulated by John Quincy Adams on July 4th, 1821:
[America]…goes not abroad, in search of monsters to destroy. She is the well-wisher to the freedom and independence of all.
She is the champion and vindicator only of her own.
She will commend the general cause by the countenance of her voice, and the benignant sympathy of her example.
She well knows that by once enlisting under other banners than her own, were they even the banners of foreign independence,
She would involve herself beyond the power of extrication, in all the wars of interest and intrigue, of individual avarice, envy, and ambition, which assume the colors and usurp the standard of freedom.
The fundamental maxims of her policy would insensibly change from liberty to force…
She might become the dictatress of the world. She would be no longer the ruler of her own spirit…
[America’s] glory is not dominion, but liberty. Her march is the march of the mind. She has a spear and a shield: but the motto upon her shield is, Freedom, Independence, Peace. This has been her Declaration: this has been, as far as her necessary intercourse with the rest of mankind would permit, her practice.
This practical wisdom may appear boring. However, organizations and governments alike must identify their assets, maintain them, and protect only what can be effectively defended. Continuous review, revision, and updates are fundamental.
The Cost of Perpetual Readiness
Sun Tzu cautioned that armies maintained in the field for extended periods deplete their own strength. Contemporary parallels include budgets exhausted by perpetual emergencies and professionals experiencing burnout due to continuous false positives.
The solution lies in cultivating a well-developed security posture rather than succumbing to ongoing panic and overreaction.
Organizations should prepare comprehensively, rest intentionally, and engage only when strategically necessary.
This sequence, prioritizing defense before offense and clarity before action, establishes the resilience that many organizations seek.
Learning From Tactical Blindness
Security breaches frequently result from overlooked fundamentals, such as unpatched systems, insufficiently trained users, and unreviewed alerts.
Similarly, the escalation of wars or crises is often attributable to unexamined assumptions.
Both scenarios arise from neglecting the primary principle of tactical disposition: understanding one’s position before determining a course of action.
Modern Application
- In cybersecurity: organizations should implement defense-in-depth strategies, automate routine checks, and prioritize cultivating awareness rather than fear. Emphasizing culture over blame.
- In governance: it is essential to align objectives with available capacity, critically assess the true cost of each commitment, and recognize that restraint can be the most strategic option.
This parallel represents a recurring pattern rather than a mere metaphor.
Practitioner’s Questions To Ask Yourself:
- Am I defending by hope instead of design?
- Which tools add noise without adding clarity?
- What assumptions have gone unchallenged for too long?
- Where has “doing more” replaced “preparing better”?
Final Reflection
While invincibility is not the explicit objective, it is often the understated result of an effective security architecture. Complete protection cannot be guaranteed. However, it can be achieved through patience and persistence. Although this approach may lack glamour, in the ongoing struggle to maintain tactical disposition, it remains essential.
Sun Tzu’s good fighter was never reckless, never idle. He shaped his defenses so well that the enemy’s attacks lost meaning.
Nations and security architects should adopt similar practices. Consistently apply the principles of tactical disposition, exercise prudent stewardship of public resources, and cultivate strength, resilience, and wisdom.
The objective is not to engage in conflict frequently, but to do so only when absolutely necessary. Making it essential to fully understand and apply this story’s principles:
“The good fighters of old first put themselves beyond the possibility of defeat, and then waited for an opportunity of defeating the enemy.”
“Thus it is that in war the victorious strategist only seeks battle after the victory has been secured, whereas he who is destined to be defeated, first fights, and afterwards looks for victory.”